Regenerative Agriculture
October 13, 2022, 12:03 pmConditions such as biodiversity degradation, soil degradation and drought in agricultural areas require a reversal of agriculture from degeneration to regeneration.
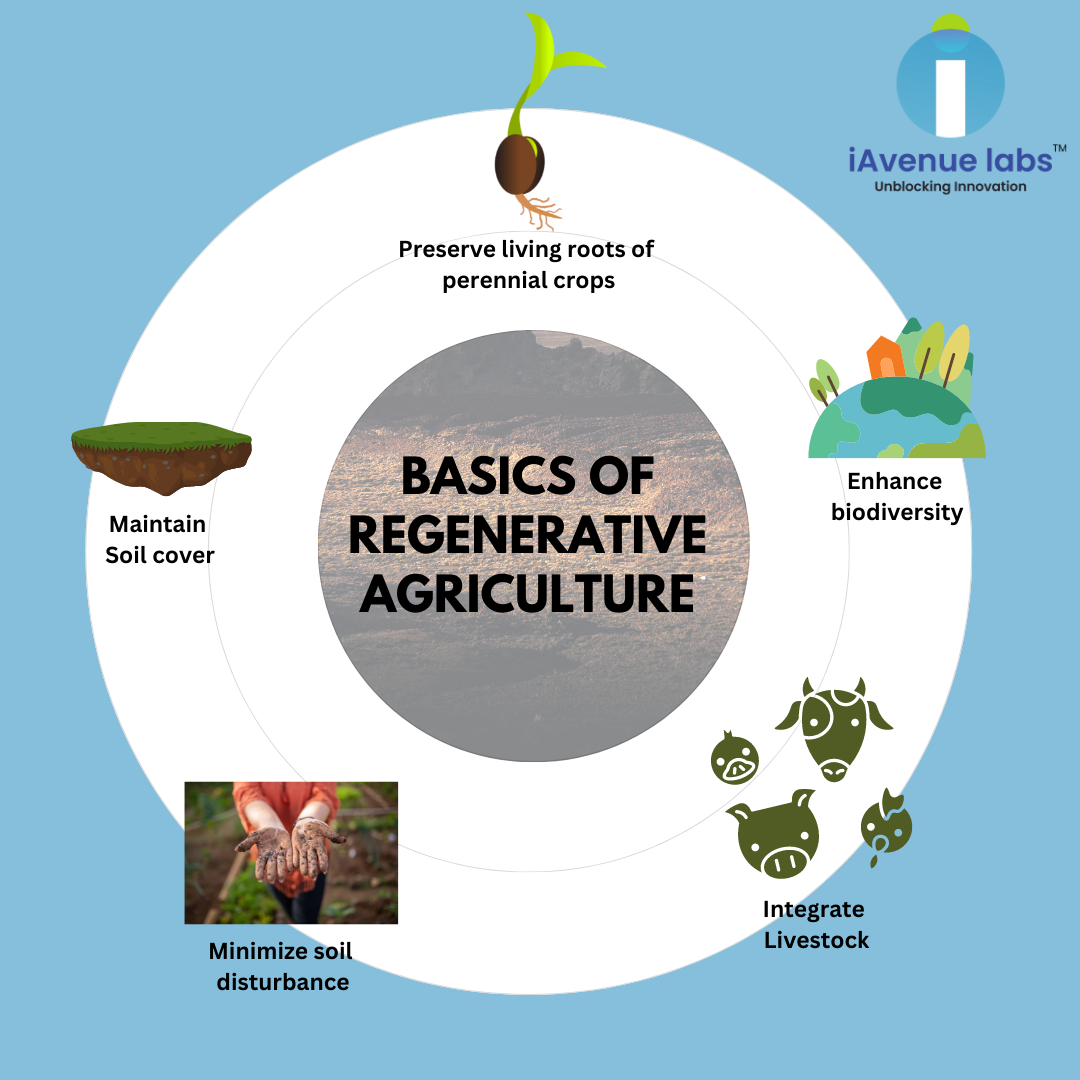
Regenerative agriculture prioritizes environmental sustainability and human health while conserving natural resources and reducing the environmental impact of agriculture, in line with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
India's potential adoption of regenerative agriculture spans at least 50 million hectares and includes irrigated, rainfed, and dry farmlands. This area can be reached through effective targeting, investment, knowledge and capacity building, and supportive measures.
Recently, agriculture has been severely impacted by climate change, and regenerative practices are struggling to reverse it. Maintaining soil vitality is a top priority for any farm, regardless of its size. This seems like a very complicated task these days, but it is known for its ability to face drought by using organic matter for its water retention capacity and increasing soil fertility.
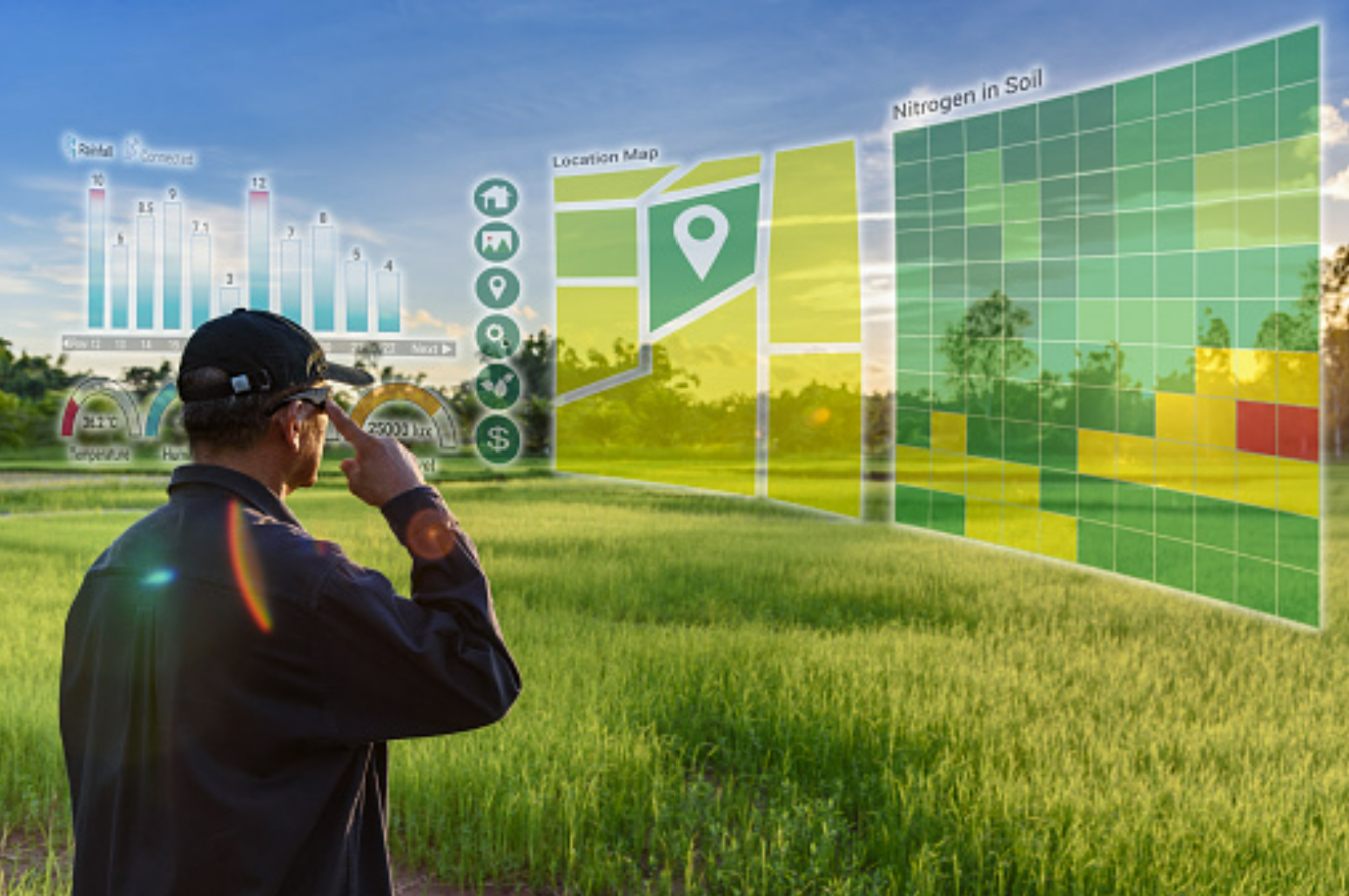
HOW FARM LAYERS, A COMPREHENSIVE FAR MONITORING PLATFORM, SUPPORTS REGENERATIVE AGRICULTURE IMPLEMENTATION?
Farm Layers provide vegetation indices, including NDVI, MSAVI, NDRE, and NDMI, to identify areas with poor vegetation and slow crop growth. Each of these indicators is more informative at certain stages of plant development, and low indicator values may indicate the presence of pests and diseases such as insects, dangerous bacteria, fungi, and other organisms. In addition, overwatering or underwatering stunts plant growth.
After reviewing the index data, the farm manager/supervisor can create a scouting job at the farm layer and use human scouts to look for potential problem areas. Only after the farm manager/supervisor inspects the critical areas and identifies the problem can the agronomist find a solution. Such procedures allow proponents of regenerative agriculture to focus primarily on problem areas identified by remote satellite monitoring, rather than inspecting entire areas of the field, which consumes both resources and time. Farm supervisors can monitor vegetation throughout the season using satellite-based field vegetation index maps. Maintaining land cover throughout the year is one of the most common tasks in regenerative agriculture. A vegetation map in a farm layer can show the condition of farmland. Areas with dense vegetation, areas with sparse vegetation, and areas without vegetation or cover (bare soil).
.png)

.png)

Food Crisis: A threat to life
Posted March 3, 2023, 1:30 pm